How Do Headers and Footers Impact Network Protocols?

Data packet transfer across networks is not possible without headers and footers, which are the building blocks of error-free communication. These components manage data segmentation across complicated network protocols, aid in error checking, and guarantee data integrity throughout data transport. Preceding the payload, headers typically include crucial control and routing information, whereas footers, if present, follow the payload and aid in data integrity verification. By comparing and contrasting header and footer services, you can get a better sense of how well protocols work, how safe data is, and how stable network systems are.
What Role Do Headers and Footers Play in Network Communication?
Understanding the Structure of Headers in Data Packets
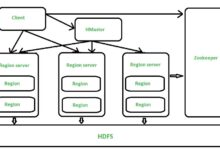
Data packet headers include crucial control information for understanding, directing, and controlling network traffic. Protocol instructions, sequence numbers, and the source and destination addresses of packets are common components of these control fields. To avoid data collisions and guarantee precise delivery, network devices use headers to figure out the best way for each packet to travel. Headers contribute to the efficiency and steadiness of the network by designating a particular route and sequence for each packet. The devices in the network rely on them to comprehend how to process and direct each packet to its destination, making them essential to the transmission process.
The Role of Footers in Data Integrity and Error Checking
Even though they are not always there, footers are vital for data integrity since they check data for errors and make sure it is correct. Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) codes are typically found in footers to verify if the data has been changed while being transmitted. In order to ensure the authenticity of the data, the receiving device verifies each packet by comparing the information in the footer with its own error-checking calculations. To guarantee error-free communication, packets might be marked for retransmission if discrepancies are detected. In low-level or data-sensitive protocols, footers help verify that sent data remains unchanged, facilitating a secure communication procedure.
Why Headers and Footers Are Essential for Protocol Efficiency
By standardizing and improving data segmentation, transmission, and error-checking, headers and footers are critical for increasing protocol efficiency. Both headers and footers are essential for packet management and routing; the former allows for precise error detection, which in turn decreases the possibility of retransmissions and data loss. Together, these features make it easier for protocols to manage data while also reducing network overhead. Consequently, protocols that value speed, dependability, and optimal resource allocation rely on headers and footers because they enhance a network’s ability to process large amounts of data with little delay.

How Do Headers and Footers Impact Data Transmission in Protocols?
Packet Segmentation and Reassembly Process
Partitioning large data files into smaller ones, with their own header and occasionally a footer, helps them to transfer more efficiently across networks. The receiving device can reassemble the packets in the correct order while maintaining the data’s integrity since the header contains information about each packet’s sequence. Faster and more controllable data transmission and reduced network congestion are both made possible by this segmentation and reassembly process. The use of headers and footers aids in this process, which in turn helps to keep network performance consistent across various data transmission protocols by ensuring correct and efficient data delivery.
Ensuring Data Security Through Encrypted Headers
A further safeguard for data transfer is the encryption of headers, which stops unauthorized parties from accessing control information. To prevent eavesdropping or manipulation, encrypted headers encrypt critical information such as IP addresses, packet sequencing, and routing details. A secure communication protocol, such as HTTPS, relies on this encryption to prevent data breaches and eavesdropping. Only authorized devices may decipher the encrypted header information. Encrypted headers protect sensitive information while it is in transit over public or open networks by locking down these control fields.
Impact of Headers and Footers on Data Flow Control
Data flow control relies heavily on headers, which play a key role in regulating the sender-to-receiver data transmission pace. Hardware can regulate data transfer rates with the help of header flow control fields like TCP window size. Headers minimize flooding the receiving device, which could cause packet loss or resend and network congestion by establishing a controlled flow rate. For a network to remain stable and efficient, proper flow control is essential for ensuring that data flows constantly and without interruption. Consequently, headers facilitate a balanced data flow, which in turn allows devices to connect efficiently without putting an undue strain on network resources.
Key Protocols and Their Use of Headers and Footers
TCP/IP and Its Header Functions for Reliable Delivery
The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol uses headers to control the transmission of data packets, which ensures a reliable connection over the network. Data ordering, error correction, and retransmission are just a few of the many features encapsulated in the TCP header. This method enables the tracking and reassembling of data packets in the correct sequence to ensure their correct arrival. Because it organizes headers to govern packet delivery, TCP/IP ensures data integrity, which is crucial for many online applications like web browsing and email.
How HTTP Uses Headers to Handle Web Data
Web browsers and servers are able to communicate more efficiently with the help of HTTP headers, which transmit metadata. Online browsers rely on headers to display online pages accurately by providing information such as content type, caching restrictions, and status codes. Web browsers rely on HTTP headers to control these exchanges in a way that makes them accurate, efficient, and easy to use. To illustrate how HTTP headers impact page loading times, consider the case of caching vs. refreshing. Therefore, headers are essential to HTTP as they simplify the transfer of web content, improve the user experience, and guarantee the accurate loading and display of every webpage.
Role of Headers and Footers in SMTP for Email Transmission
When sending email from one server to another, SMTP uses headers to structure and guide the transfer. To ensure that messages arrive in the correct mailbox, email headers include details such as the sender’s and recipient’s addresses, as well as a timestamp and subject. Even though they are not often utilized, SMTP footers provide the option to add end-of-message indicators or checksums to provide further security. With this framework in place, you can rest assured that the message will arrive unaltered and intact. Because SMTP protocols employ headers to organize and safeguard email data, users can send and receive emails without worrying about interruptions or data loss. Thanks to this, emails can flow between networks with ease.
Conclusion
Network protocols would not function without headers and footers, which serve as verification and navigational aids to ensure correct data transfer. Footers improve data integrity with error-checking functionalities, whereas headers provide control and routing information. Recognizing the difference between header and footer roles clarifies their impact on protocol efficiency and security, ensuring smooth data transmission across networks. These components help keep network communications steady, fast, and reliable by aiding with segmentation, security, and flow control. As an example of the careful design of protocols that create efficient and trustworthy connectivity across varied network systems, they play an important role in error-checking and data management.